Back in the day, users were quite straightforward in their needs for digital products, focusing mainly on basic functionality. Their expectations for overall appearance and user experience were quite limited. But things have changed. With market development and improvements in people's living conditions, the demand for functionality of digital products significantly increased in recent years. People began to seek various needs, including usability, visual aesthetics, and diversity. Consequently, this change in attitude birthed the concept of UI and UX design.
The impact of UI design is profound, influencing various aspects of user interaction and overall user experience of a product. So, what's UI design exactly? Why does it matter so much? And how's it different from UX design? Let's get a comprehensive understanding of UI design in this article.
First, we should know that "UI" actually stands for "User interface". It's the graphical user interface of a software, an app, website, or any digital device that a human interacts with.
UI design, therefore, is the process that designers build these digital interfaces. It focuses on how things look and feel on screens, like the colors users see, the animations they interact with, the buttons they press, or the text they read.
So, in simpler terms, UI design is the visual magic, making sure everything looks great and works seamlessly when you interact with it.
The second part of UI design is its basic elements. UI elements can generally be categorized into four main types:
Input Controls allows users to inputting information into the system. Its examples include buttons, text fields, checkboxes and radio buttons.
Buttons: It's an interactive element that users click to initiate actions or submit information within an application or website, such as submitting a form, saving changes, or navigating to another page.
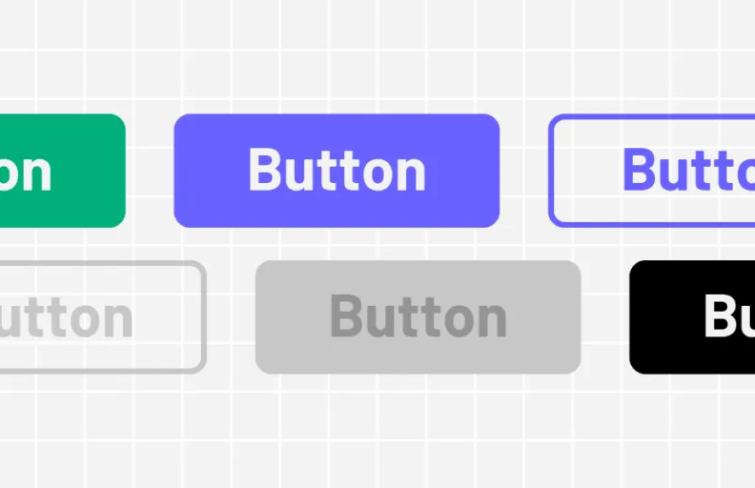
Text Fields: It allows users to input alphanumeric characters. They are commonly used for tasks like entering text, numbers, or other data, such as usernames, passwords or search queries.

Checkboxes: It allows users to select multiple options from a list. They are often used in forms and settings to enable users to make multiple selections.
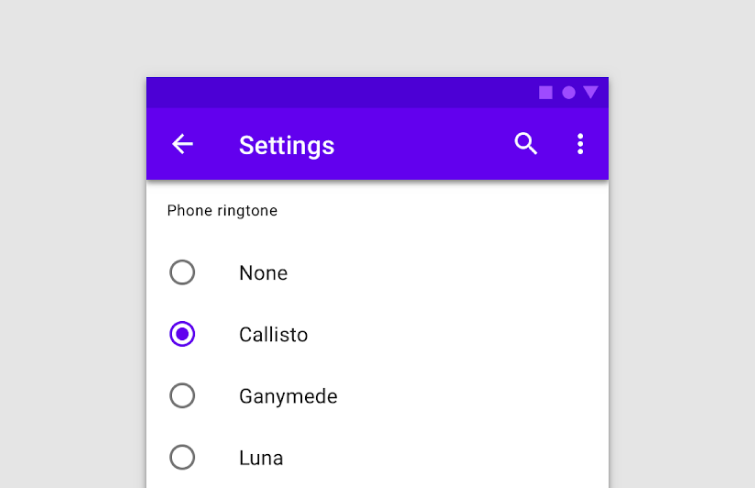
Radio Buttons: Radio buttons are used when users need to select a single option from a list. Unlike checkboxes, users can only choose one radio button within a group.
Navigational Components help users move around the application or website. Its examples include menus, breadcrumbs and sliders.
Menus: It provides a list of options for users to navigate through an application or website. They can be horizontal or vertical and may include dropdowns for sub-options.
Breadcrumbs: It shows the user's current location within a hierarchical structure and provides an easy way to navigate back to previous levels.
Sliders: Sliders allow users to select a value within a specified range by moving a slider control. They are often used for settings like volume control or selecting a price range.
Informational Components provide information to users. Its examples include notifications, tooltips, progress bar and icons.
Notifications: Notifications inform users about events, updates, or errors. They can be displayed as pop-ups, banners, or in other formats.
Progress Bars: Progress bars visually indicate the completion status of a task, providing feedback to users about the progress of an operation.

Tooltips: Tooltips provide additional information or context when users hover over or click on a specific element. They help clarify the purpose or function of an element.
Icons: Icons are visual symbols that represent actions, objects, or concepts. They are used to enhance the visual representation of elements and aid in quick recognition.

Containers organize and structure the content on the interface. Its examples include accordions and tabs.
Accordions: Accordions allow users to expand or collapse sections of content, providing a way to organize and present information in a compact form.
Tabs: Tabs organize content into multiple sections, making it easy for users to switch between different views or categories.
As the market growing, digital products have become an integral part of our daily lives. The significance of UI design in app development cannot be overstated. It's crucial for the long-term viability of applications in a competitive market. Here are some key points highlighting the crucial role of UI design:
The user interface is the first point of contact between a user and a product. A visually appealing and well-organized UI creates a positive first impression, capturing the user's attention and encouraging further exploration.
UI design directly impacts the user experience. UI design focuses on creating interfaces that are intuitive and easy to navigate. A well-designed interface enhances usability. When users can easily understand and interact with an interface, they are more likely to achieve their goals efficiently, which can significantly reduce user frustration and minimize errors. Consequently, satisfied users are more likely to return to a product, increasing user retention and contributing to long-term success.
The design elements used in a UI, such as color schemes, typography, and iconography, contribute to the overall brand identity. Consistent and cohesive design reinforces brand recognition and helps establish a brand's personality. Moreover, a well-designed UI can also be a differentiator. If users find a product's interface more user-friendly and visually appealing than that of competitors, it can contribute to gaining a competitive edge.
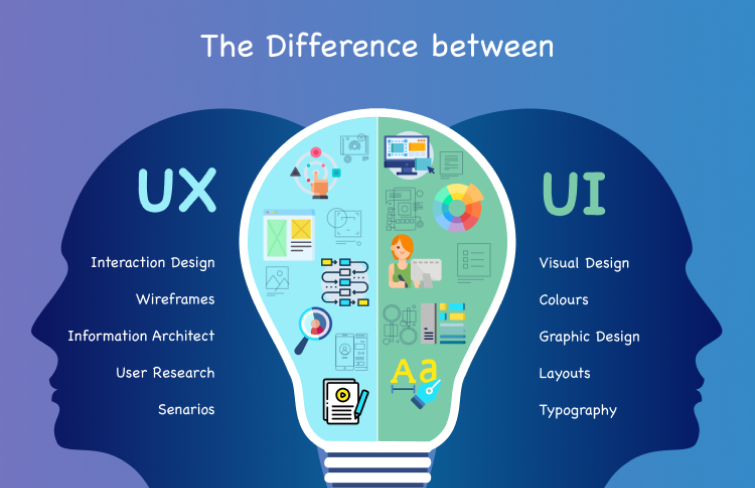
You must have been wondering about the difference between UX design and UI design. UI and UX design are both crucial to a product and work closely together. But they are different and focus on different aspects of the overall user experience.
UI Design: UI design stands for “user interface design”. It's primarily concerned with the visual elements of a product.
Focus: Look and feel of the interface. It involves designing the layout, colors, typography, and interactive elements that users directly interact with.
Goal: To create visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces that are easy to navigate and understand.
UX Design: UX design refers to the term “user experience design” . It encompasses the entire user journey, from the first interaction to the final experience.
Focus: Functionality and overall user experience. It involves understanding user needs, creating user personas, developing user journeys, and designing the interactions, overall flow and structure of the product.
Goal: To create a positive, efficient, and enjoyable experience for users.
As we already know, the goal of UI design is to create visually appealing, user-friendly interfaces that enhance the overall user experience. Accordingly, there are some key design skills needed to achieve this goal efficiently.
Graphic design is like the ABCs of the digital world's visual language. It uses pictures, icons, fonts, and layout to share info and spark feelings. Learning basic graphic design is a bit like learning the alphabet – it's the starting point for creating cool and good-looking visuals. Just as letters make words, graphic elements come together to make awesome messages online.
Color theory is a fundamental concept in amost every kind of design. It explores how colors interact with each other and how they can be combined to create aesthetically pleasing and effective visual compositions. It involves understanding the properties of colors, their relationships, and the psychological impact they have on individuals.
Typography, the art of font selection and arrangement, is crucial in UI design for ensuring readable and visually pleasing text. The primary focus is on readability and legibility. Different fonts have different levels of readability, like sans-serif fonts being good for screens, while serif fonts work better for print. You also need to choose fonts for different parts of your design, like headings and buttons. Typography helps create a visual hierarchy, highlighting important stuff and guiding users through the content.
Layout and composition are vital for organizing content in a user-friendly manner. They involve arranging elements logically, utilizing grid systems for consistency, and implementing responsive design for adaptability across devices. Proper spacing, alignment, and hierarchy can significantly enhance readability.
Just as an artist uses brushes to bring their vision to life on canvas, designers use tools like Mockplus DT, Figma, , Adobe XD or Sketch to turn design concepts into tangible assets for developers. Proficiency in these tools enables designers to seamlessly translate ideas into interactive and visually appealing user interfaces.

Understanding and empathizing with users' needs, preferences, and behaviors is crucial for creating interfaces that truly resonate with them. By putting yourself in the users' shoes, you can design interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive, user-friendly, and aligned with their expectations.
Good UI design usually depends on teamwork. UI designers have to work closely with cross-functional teams, including developers and product owners. So they must equip themselves with effective collaboration and communication skills. This teamwork brings different perspectives, making the design creative and problem-solving.

Design principles are fundamental guidelines that help designers create effective and user-friendly interfaces. Here are some key UI design principles:
"A user interface is like a joke. If you have to explain it, it's not that good." - Martin Leblanc
This quote encapsulates a profound truth in UI design. Simplicity is a fundamental principle in UI design. Keeping interfaces clean and straightforward helps users focus on their tasks without confusion. Each element on the screen should contribute significantly to the user experience, with unnecessary elements removed. Only in this way can users quickly find what they’re looking for without any unnecessary complexity.

UI designers should strive for both visual and functional consistency in elements like fonts, colors, buttons, and icons. It means that designers must make sure that the same elements represent the same function or action in all contexts. This helps users easily understand and navigate the interface. Designers often use a design system to effectively ensure consistency in the visual elements across different projects.
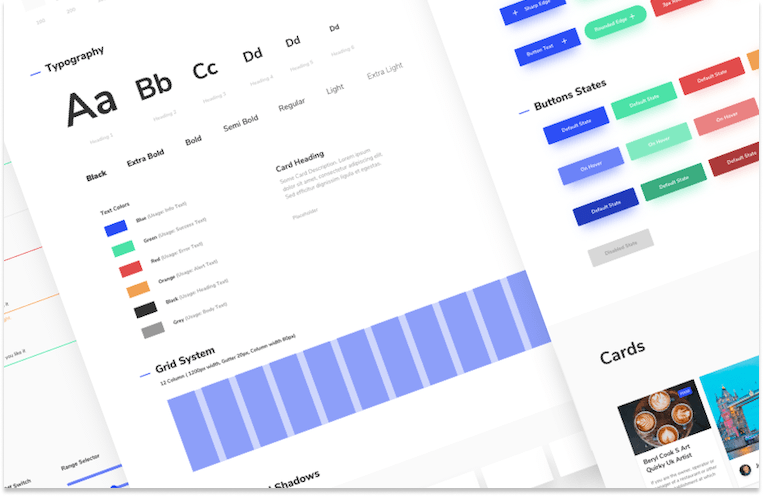
To achieve a truly minimal and efficient UI, it's crucial to establish a clear hierarchy for informations and functions. Emphasize the most important informations and functions by using size and scale, color and contrast, typography, and whitespace and more. For example, if A and B are priorities over Z, designers will often make them more prominent to guide user focus by adjusting sizes or using distinct colors.
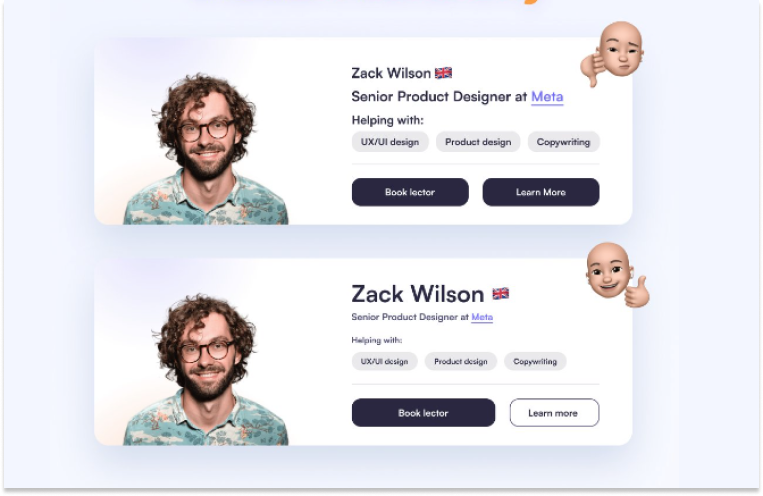
Design conventions are proven methods that have stood the test of time in helping users reach a specific goal. Users have got accustomed to them and now expect them to work a certain way. Most of time, designers should keep elements where users expect them and follow these common design conventions. For instance, finding the menu at the top of a webpage is a common expectation. UI designers should use this familiarity to create interfaces that feel comfortable and user-friendly for the most of users.
Please note: These design conventions are not mandatory but are widely adopted because they have proven to be effective. Designers still have the flexibility to deviate from conventions only if they have a better idea. If not, it's a good idea to stick with the usual conventions.
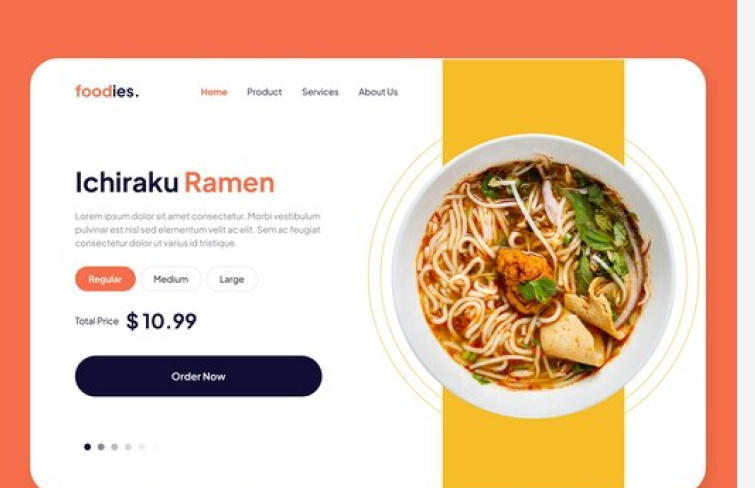
Always provide immediate and informative feedback to users' actions as they move through the interface. When users interact with a system or interface and receive no response, it can lead to feelings of uncertainty and anxiety. Whether through visual cues, messages, or other forms of acknowledgment, a responsive interface helps create a more confident and positive user experience.
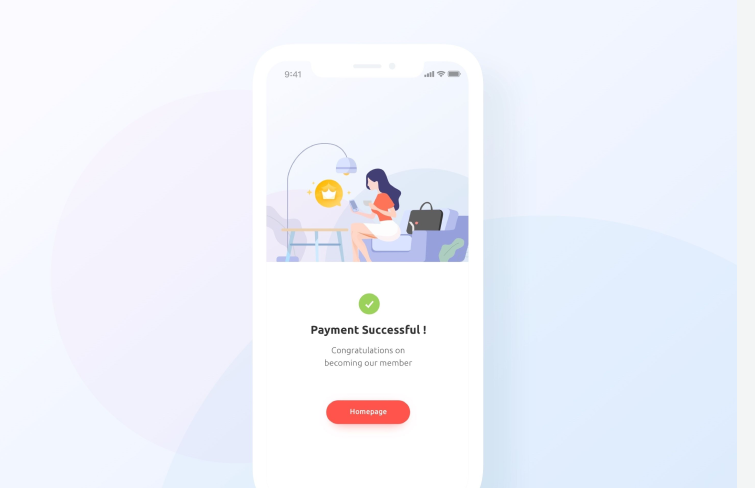
Creating an effective website means making it accessible to everyone. The WCAG Web Accessibility Initiative offers UI designers specific guidelines. A key principle is not relying on a single element for communication. For instance, instead of just using "Yes" and "No" buttons, adding checkmarks and X marks, and using distinct colors like green and red, can enhance communication. This approach caters to users with color blindness or different reading skills, ensuring a more inclusive and navigable website.

With so many UI design tools out there, each with its own features, picking the right one is crucial for an effective design process. Here are some popular UI design tools in the market.
Figma is a web-based design tool that allows collaborative design in real-time. Its core strength lies in seamless design collaboration, enabling multiple users to work on a design simultaneously.

Mockplus is a web-based design tool that covers almost all the key features of Figma. But it's much cheaper than Figma. It offers a free plan for everyone with limited features. And for its paid plans, it costs only $8 per user per month, while Figma charges $12-$45 per user per month. Moreover, it also provides one central place for whole team to design, animate, collaborate and handoff.
Sketch is a vector-based design software for macOS, widely used for UI and web design. Sketch is favored for its focus on the design needs of digital interfaces, offering symbols, artboards, and a thriving plugin ecosystem.

Adobe XD is a comprehensive design and prototyping tool that integrates seamlessly with the Adobe Creative Cloud. Adobe XD is known for its smooth workflow and integration capabilities.

Photoshop is a versatile graphic design tool used for a wide range of creative projects, including web design. It's not exclusively a UI design tool, and its core strength lies in image manipulation and intricate design work.

Adobe Illustrator is a vector-based graphics processing tool. It's widely used for vector graphics and is suitable for creating detailed UI elements.

As we move forward in UI design, designers will face diversified demands due to technological advancements. For example, for decades, tangible screens have been the primary canvas for UI designers, shaping how users interact with digital information and experiences. However, the landscape is undergoing a transformative shift as technology evolves. A significant indicator of this shift is the growing prevalence of touchless interaction such as voice-controlled digital assistants and AR/ VR devices like Apple Vision Pro. UI designers will have to consider how to deliver excellent user experiences on these touchless interaction devices. For example, in designing UI for AR/ VR devices, it's crucial to think like an industrial designer, keeping the human body at the center of experience. What’s the length that an arm has to extend to grab something? When standing, what should the average height of an object be so users can interact with it intuitively?

Besides, the way we design UI is also going to change rapidly with the power of AI. As ChatGPT gained widespread attention in 2023, the AI landscape experienced a surge in innovation, introducing a plethora of diverse generative AI tools such as Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and others. This rapid evolution has significantly impacted the field of UI design and rapidly changing the way we design products and services. As AI continue to develop, they will have an even greater impact on UI design.
We are likely to see more and more enhanced personalization through user behavior analysis, the rise of generative design for creative expression, and predictive design assistance for accelerated workflows in the upcoming future. AI is undoubtedly going to shake up traditional content and service production methods.

In conclusion, UI design is like the behind-the-scenes hero of websites and apps. By carefully balancing buttons, layouts, and other elements, UI design ensures your product looks good and easy to explore and navigate through. So , if you aim to please, captivate, and keep your customers satisfied with your digital products, it's essential to invest in UI design.
Ok, that's all for this article. Hopefully, you now have a clear idea of what UI design is and what skills are needed to create visually appealing, user-friendly user interfaces.