Behind every great product we use today is a development team that brought it to life. Product management is a glue that connects design, development, and marketing. As the demand for skilled product managers continues to surge, many individuals are now setting their sights on this dynamic and rewarding career path. So, if you're ready to embark on a journey toward becoming a product manager, this article is for you.
This article explains what product management really is and how to get into this field.
A product manager is a professional responsible for guiding the development and management of a product throughout its lifecycle. It's possible to say that a product manager serves as the "CEO" of a product—a product manager ensures that a product meets the needs of its target audience and aligns with the overall goals and strategies of the company.
Product managers must possess a combination of business acumen, technical understanding, and strong communication and leadership skills to excel in this role.
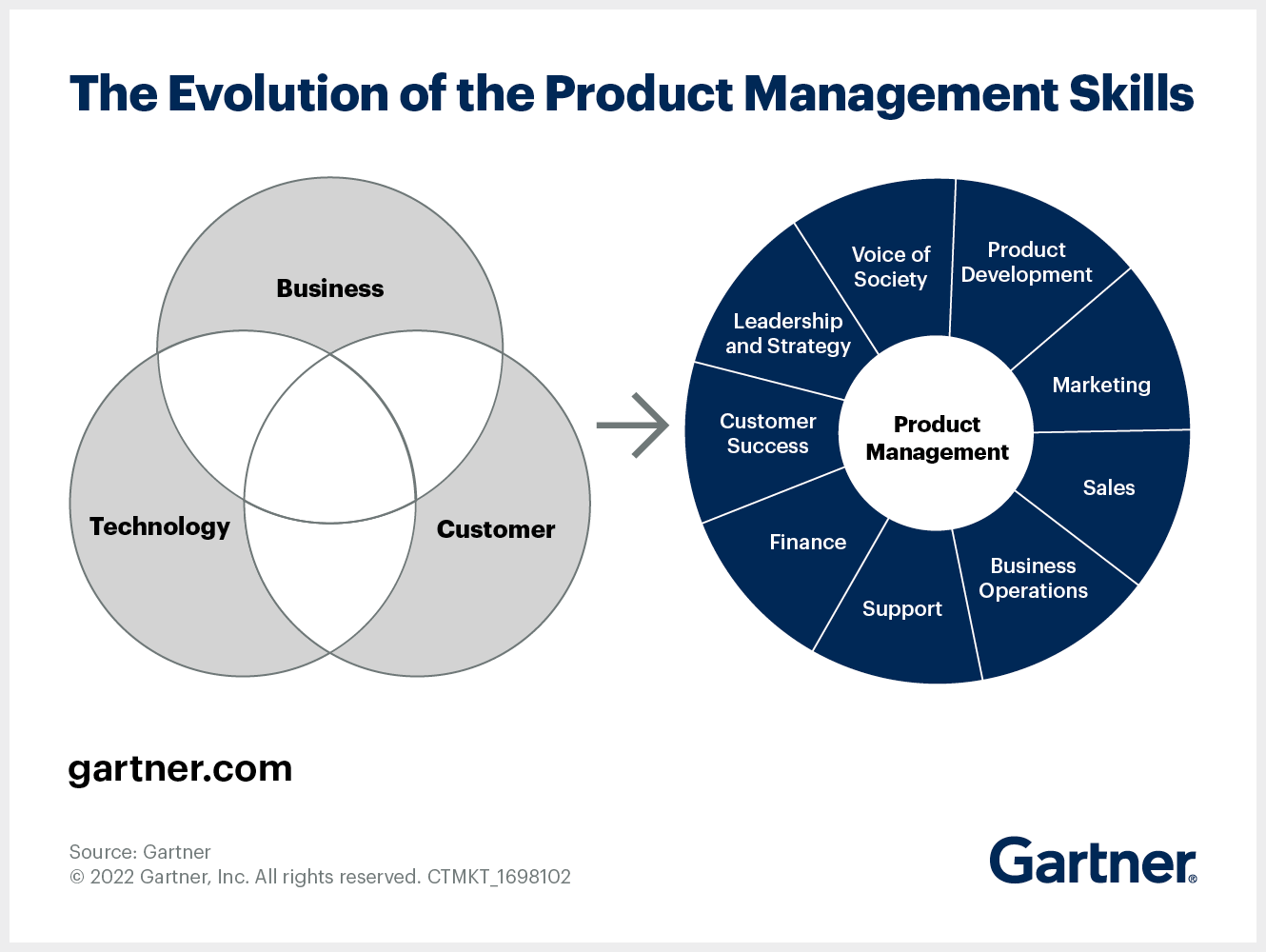
Product management skills. Image by Gartner.
For individuals with no prior experience or achievements, crafting a standout product manager resume can still be achieved by emphasizing relevant coursework, personal projects, and transferable skills to demonstrate your potential for success in the role.
Let's review the essential qualities to possess if you want to become a product manager:
Product management is all about finding optimal solutions to specific problems. That's why product managers must be adept at identifying problems, analyzing data, and proposing solutions to meet customer needs and business goals.
Product managers should be able to set short-term and long-term goals for a product. This ability will help the manager to create a product strategy and a roadmap with the specific milestones that the team should achieve.
Product managers should understand and empathize with customers. Having a clear understanding of who will use your product (target audience), why they might want to use it (user goals), and how exactly they will do it (use case scenarios) will help product managers to find optimal product design decisions.
It's not enough to know how the product should be built; convincing team members to follow a specific path when creating a product is vital. Leadership skills are crucial to guiding cross-functional teams and stakeholders. Strong verbal and written communication skills will help a product manager convey ideas, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and present product strategies.
The product design landscape is changing constantly. The ability to adapt to changing market conditions and iterate on product strategies is crucial. It's vital to stay updated on industry trends and emerging technologies.
While not mandatory, having an essential understanding of the technologies used in your project can be advantageous, especially in the digital product design field. If you're familiar with software development methodologies and have coding skills, it will make your product manager's life much easier since you will be able to communicate effectively with engineering teams.
Product management doesn't always follow a rigid, universally defined set of stages, as the process that the product managers use can vary from one organization to another and depends on the nature of the product being developed. However, a common framework for product management often includes the following seven stages:
Idea generation, or ideation, is a crucial stage of product management because, in this initial stage, product managers identify potential product ideas. These ideas may come from various sources, including market research, customer feedback, industry trends, and internal stakeholders. The goal is to explore these ideas to determine their viability & alignment with the company's goals and frame a concept that will later be turned into a product.
Once ideas are generated, product managers conduct extensive market research to evaluate if it's possible to turn these ideas into products that customers will buy. During the research phase, product managers understand customer needs, market trends, and competition in a business niche. This stage involves validating the concept by gathering data and feedback from potential customers to determine whether there is a market demand for the proposed product.
After validating the concept, product managers work on defining the product's specifications— features the product will offer along with the time required to implement the features. Product managers create a product roadmap and prioritize features based on factors like customer value, business goals (business objectives the organization tries to achieve with this product), and technical feasibility (how easy or hard it is to build a feature). This stage also involves setting clear objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) for the product that will be used to evaluate the product development outcome.
In this stage, product managers collaborate with design and development teams to build the product. They oversee the design process, ensuring that the product is created in accordance with the product's vision. Product managers work closely with designers to ensure the product offers a proper user experience. Once the design is finalized, product managers work with the engineering team to ensure the product is implemented correctly.
Testing is an essential part of the product development process. During this phase, the team ensures that the product meets quality standards and functions as intended. The testing phase might include various activities like quality assurance procedures (testing whether the product functions as intended) and usability testing (evaluating how easy or hard it is for end users to use a product). Product managers coordinate testing efforts with QA and usability testing professionals and gather feedback from them. These activities aim to identify and address any issues or bugs before the product reaches the market.
The product launch is a critical phase where the product is introduced to the market. Product managers work with marketing and sales teams to develop a go-to-market strategy, including product positioning, pricing, and promotional activities. They also monitor the product's performance during the launch phase to identify things that customers like and dislike in a product.
Product design is a never-ending process. After the product is launched on the market, the work of a product manager continues. They gather and analyze data on how the product is performing, track critical metrics & evaluate them according to the KPI defined during the planning stage, and collect feedback from customers and stakeholders. Based on this information, they make informed decisions about further improvements and iterations to the product. This stage involves ongoing maintenance (fixing bugs in the product) and planning the scope for the next version of the product (i.e., selecting features that will be added to the product in the next release).
It's important to note that the process that product managers follow is iterative. Product managers must continuously adapt to the feedback they receive from the users, changing market conditions and evolving business objectives.
Becoming a product manager without prior experience can be challenging, but it is possible with the right approach and dedication. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to become a product manager without prior experience:
The first thing you need to do is understand the role and responsibilities of a product manager. You need to have a clear understanding of what a product manager does (tasks and duties) so you can master the skills and get the required qualities that make a successful product manager. To get a general idea about product management, you should start reading popular books about the topic. Below are the top three highly recommended books about product management.

"Inspired: How To Create Products Customers Love" by Marty Cagan. This book is often considered a must-read for aspiring product managers. Marty Cagan, a partner at Silicon Valley Product Group, shares insights and best practices from his extensive experience in the field. He covers key topics such as product discovery, product development, and effective team collaboration.

"Lean Product and Lean Analytics" by Ben Yoskovitz and Alistair Croll. This book combines two highly regarded titles—Lean Product and Lean Analytics—in one volume. "Lean Product and Lean Analytics" offers practical guidance on creating successful products while emphasizing data-driven decision-making. It covers Lean Startup principles, product metrics, and techniques for building products that customers truly want.

"Hooked: How to Build Habit-Forming Products" by Nir Eyal. Nir Eyal's book delves into the psychology behind creating habit-forming products. Understanding how to design products that engage users and keep them coming back is a fundamental aspect of product management. "Hooked" provides valuable insights into building products that users can't resist.
Suppose you have a clear idea about the organization you want to apply to. In that case, you should read the job description to learn what specific skills the organization is looking for in candidates for the product manager role.
Once you learn about the role, you need to evaluate your existing skills and experiences. As was mentioned before, product managers need a combination of problem-solving, marketing, technical, and interpersonal skills. You need to analyze your past experience and identify areas where you have strengths and areas where you need to develop new skills. Invest the time in filling the knowledge gaps. The most straightforward way to do that is to apply to product management courses, and we share the top 5 courses for product managers below.
To become a product manager, you'll need to develop or enhance communication, analytical, marketing research, technical proficiency, and product design skills. Speaking of which, explore the internet (YouTube, LinkedIn, Reddit) as it is the richest resource when it comes to developing skills. While on your voyage to get the best out of resources, make sure to connect to a reliable home WiFi like the one from Spectrum. It offers high-speed but low-cost internet plans along with responsive Spectrum customer service. Get Investing in communication skills will improve your ability to convey ideas clearly and effectively. Strong analytical skills will help you analyze complex data and make data-driven decisions. Technical knowledge will help you better understand software development so, at the end of the day, you will speak the same language as designers and developers. It's vital to know how to conduct market research, gather customer feedback, and turn it into insights that can be used to make the product better. Lastly, you need to gain a solid understanding of user experience and user interface design principles to evaluate design decisions proposed by the design and development team and maximize chances for creating user-centered products.
When organizations hire product managers, one of the first things they check is the candidate's portfolio. A portfolio is a collection of projects a candidate worked on, structured in case studies. One of the typical questions that many people who want to start in the product management field ask is what to put into a portfolio if you don't have professional experience. Even without professional experience, you can work on personal projects or collaborate on volunteer initiatives to build a product management portfolio. Document your involvement in project management, market research, product ideation, and any relevant product design tasks. Frame your experience into stories that showcase your ability to solve problems and make decisions.
When it comes to career opportunities, the best positions in organizations are rarely listed on job-hunting websites. Most of the time, such positions are spread by word of mouth—people who work in organizations try to recommend the professionals they know who will be the best fit for the role. This practice is called referral hiring, and it's widespread in large organizations. To maximize your chance of getting a great job, you must build a solid network of contacts. The easiest way to achieve this goal is to participate in offline and online events. Attend industry events, conferences, and meetups related to product management. It will give you a chance to connect with professionals in the field. Once you know people, you can grow your network of contacts on LinkedIn. Join product management groups or forums to engage in discussions and gain insights.
Once you have gained essential skills & built a portfolio, you can start applying for product assistant or associate roles. Look for entry-level positions that are related to product management and have transferable skills. These roles may include associate product manager (a professional who assists lead product managers with managing large products that need multiple supervisors) or business analyst assistant. These positions can provide valuable experience, minimize the risk of failure in this field (since you will be working with an experienced person who manages the product), and become a stepping stone into a product management career.
Prepare for the interview to maximize your chances of getting a job offer. Study common product management interview questions and practice your responses. Be prepared to discuss your portfolio projects and how your skills and experiences align with the role. Once you receive an invitation to the interview in a specific company, learn as much as possible about the company and its challenges. Read job descriptions to understand what specific skills the company is looking for in candidates, and be prepared to answer how your professional experience aligns with the company's goals.
Landing your first product management role may take time and persistence. You will likely get a lot of rejections in the beginning, but it's okay; it's a natural part of the hiring process. It's vital not to be discouraged by rejection; keep applying, learning from each failure, and refining your skills.
There are many excellent product management courses available that can help you get started in this field. Here are some of the best product management courses to consider:
Marketing is an integral part of product management. No matter how good your product is, it will fail on the market if people aren't willing to pay for it. This course provides a strong foundation in marketing principles for product managers. You will better understand branding principles and their application to product marketing, customer behavior, and go-to-market strategies.

"Introduction to Marketing" by the University of Pennsylvania (Coursera)
While project management and product management are not the same thing, having solid project management skills is vital for any successful product manager. Google offers a comprehensive project management certificate program on Coursera. You will learn the foundations of project management, such as how to estimate time and budgets, run effective meetings with stakeholders, and apply Agile and Scrum frameworks in the product design process.
"Google Project Management Certificate" (Coursera)
This course offers a comprehensive overview of product management. You will learn core skills that make up the entire product management process—from ideation to market research. At the end of this course, you will be able to quickly test & validate your product idea over a weekend, effectively lead developers & designers and manage stakeholders.
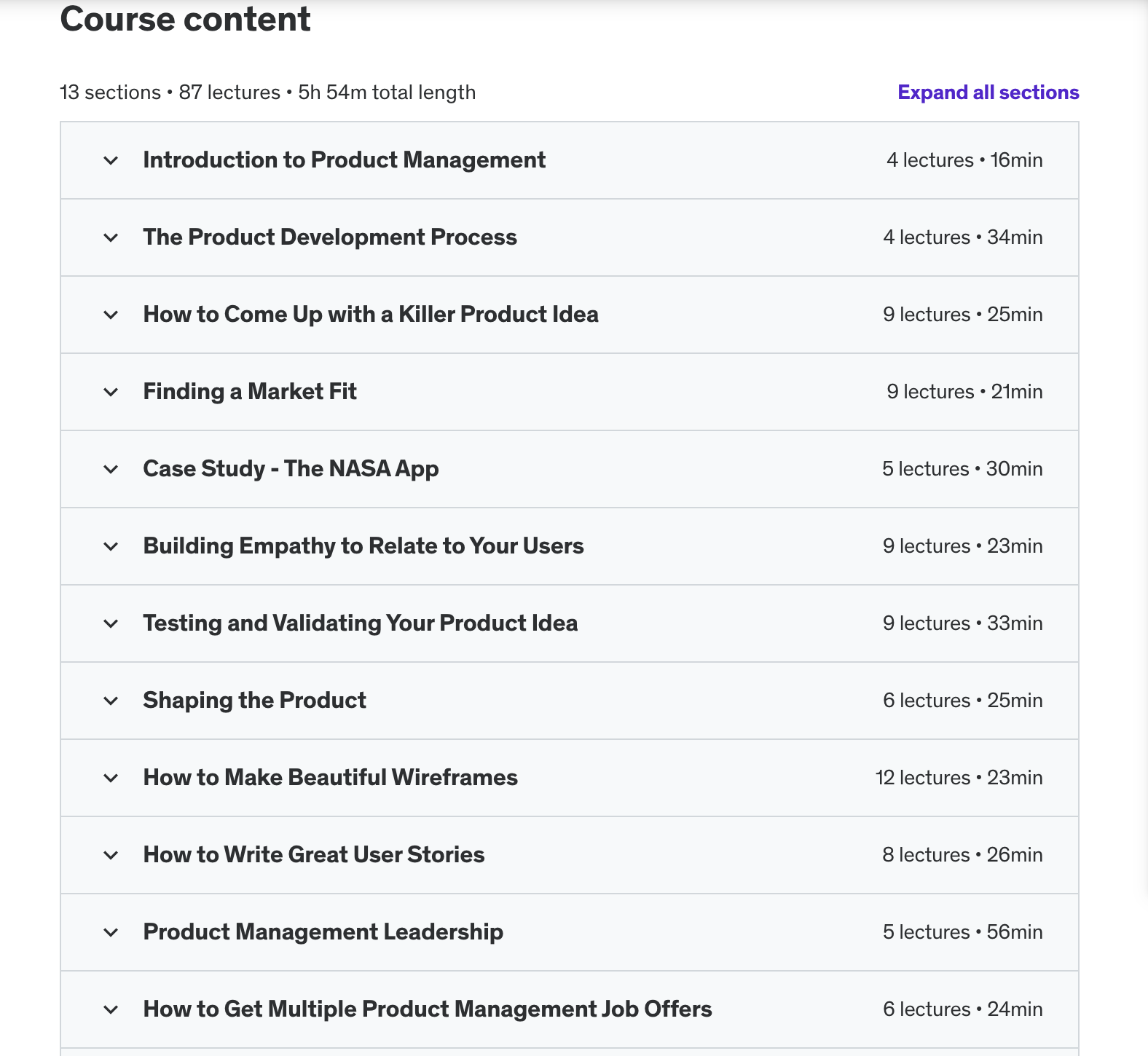
"The Complete Product Management Course" , course content.
General Assembly offers a range of courses related to product design and management. Their programs often include guest speakers from the industry. This course will teach you how to balance business viability, technical feasibility, and customer desire to lead products and features toward long-term success. You will learn this information from the best experts in the space.
"Product Management Course" (General Assembly)
Stanford University runs various courses for product managers and business owners. This course is focussed on seasoned product managers. It will help you develop strategic frameworks, customer empathy, and communication and leadership skills to help you move from product management to the C-suite (Chief Product Officer).

"Innovative Product Leadership" by Stanford University
A product manager's salary can vary widely depending on factors such as their location, level of experience, the industry they work in, and the specific company they are employed by. An entry-level product manager with limited experience might earn an annual salary ranging from $60,000 to $100,000 in the US, depending on the location and industry. Product managers with a few years of experience typically earn salaries ranging from $100,000 to $150,000. Senior product managers with extensive experience and a proven track record of success can command salaries ranging from $130,000 to $200,000 or more, with the potential for bonuses and stock options.
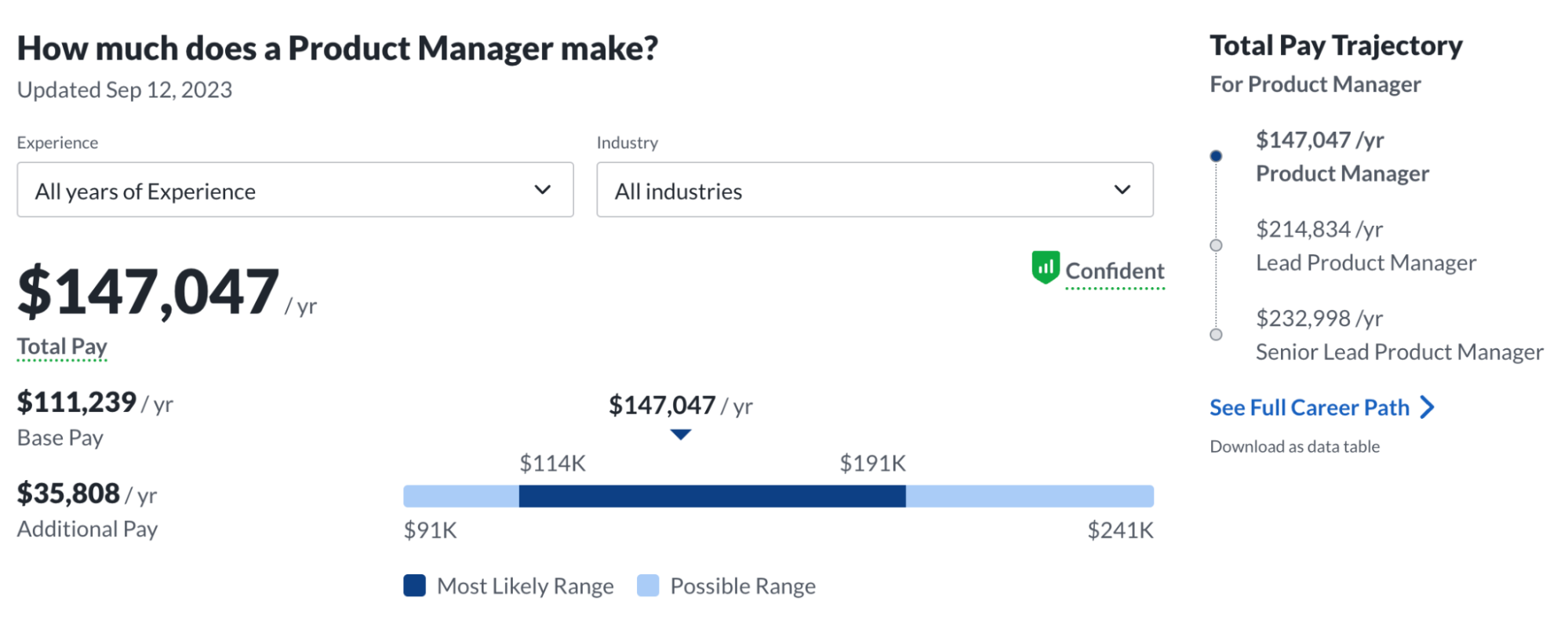
How much does a product manager make? Image by Glassdoor.
The journey to becoming a product manager is both challenging and rewarding. It demands a blend of skills, from effective communication and strategic thinking to market analysis and leadership. But no matter whether you're a recent graduate or a seasoned professional willing to move to this field, your dedication, adaptability, and persistence will be your greatest assets on the path to a successful product management career. Embrace the opportunities for growth, keep refining your skills, and trust in your ability to make a meaningful impact in the dynamic world of product management.
While product management can be stressful, it's important to note that stress levels can vary significantly from one company and role to another. Some organizations prioritize work-life balance and provide support and resources to help product managers manage stress. Additionally, experienced product managers often develop strategies for handling stress, such as effective time management, delegation, and self-care.
Getting into product management can be challenging, but it's not impossible. The difficulty of breaking into this field often depends on several factors, including your background, skills, networking, and persistence. It's important to note that the path to becoming a product manager can vary from person to person. Some individuals transition into product management relatively quickly, while others may need to gain more experience and skills before securing a product management role. Your unique combination of skills, experiences, and determination will play a significant role in your journey.
Product managers come from a wide range of educational backgrounds, and there is no one-size-fits-all degree that is considered the best for this role. Instead, what matters most is a combination of skills, experience, and knowledge relevant to the responsibilities of a product manager. That said, certain degrees such as business analytics, computer science, psychology & behavioral science, and marketing can be particularly advantageous.
Product management typically does not require coding as a mandatory skill, but having some level of technical expertise and coding skills can be beneficial in certain product management roles, especially in technology-driven companies.
 Mockplus RP
Mockplus RP
A free prototyping tool to create wireframes or interactive prototypes in minutes.
 Mockplus DT
Mockplus DT
A free UI design tool to design, animate, collaborate and handoff right in the browser.
