It's nearly impossible to imagine a design process that doesn't have a prototyping phase. Before team members invest time and money in building an actual product, they want to ensure that the design is both valuable and usable for the target audience, and prototyping helps to achieve this goal. Once product creators build a prototype, they can test it with real users to ensure that users can interact with it without any problems. Most teams want to learn techniques that will help them build prototypes faster. Rapid prototyping is one of the techniques that promises precisely that.
In this guide, we will discuss a technique called rapid prototyping that can help a team to speed up the prototyping process.
The word "rapid" is likely to give you an idea that "rapid prototyping" is a technique of creating prototyping fast.
The term "rapid prototyping" originates from manufacturing. In the manufacturing industry, the cost of production is high, and designers often create 3D models of the future product to validate a design. Not only the cost of a product is what matters, but also the time required to build a product can be significant. Creating an actual physical product takes months or years, but creating a 3D model of a product can take a few hours. That's why designers prefer to create a 3D model, test it before production, and only after that invest in creating a real product.
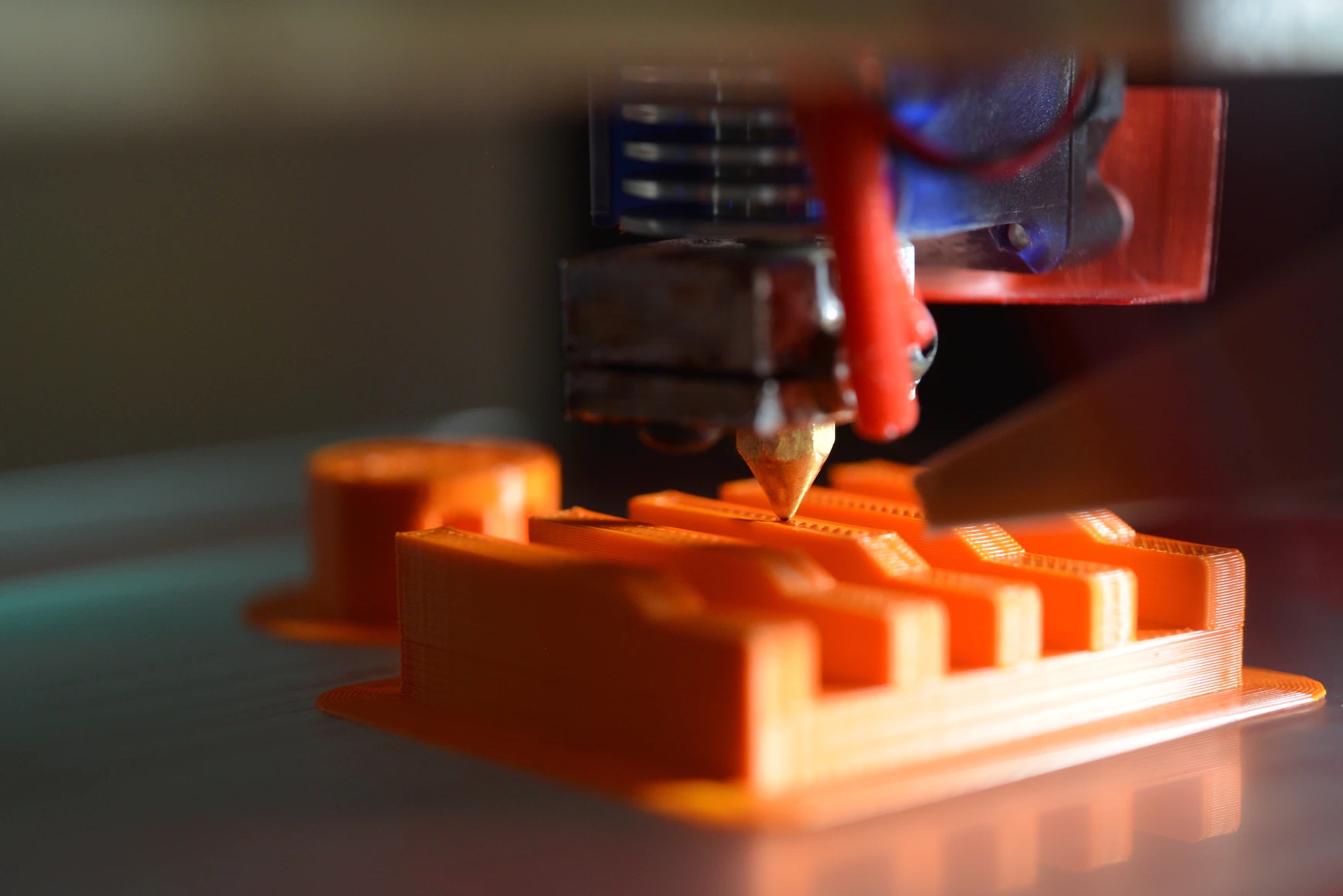
Using 3D printing to create a physical prototype. Image by Gavin Allanwood.
In digital design, rapid prototyping is a fast and cost-effective way of creating a working version of a future product.
Designers create a prototype using design artifacts they already have. During the early stages of the product design process, the team can create a prototype from sketches or wireframes, while during the later stages, the team can use pixel-perfect mockups. Prototypes are not necessarily digital; it's possible to use paper prototypes to communicate design decisions or even try a mixed format. For example, the team can turn paper prototypes into digital artifacts by simply taking photos of sketches and uploading them to design tools.
A popular misconception about rapid prototypes is that they have low quality. Traditionally, rapid prototyping was associated with low-fidelity design simply because no tools allow fast and inexpensive prototyping. But the situation changed drastically in the last few years. Modern design & prototyping tools streamline the design process and allow designers to create high-quality prototypes in no time.
Speed of creation is by far the main advantage of rapid prototyping. It takes significantly less time to create a prototype using this technique.
Here are a few benefits that rapid prototyping can bring to the design process:
A design team can quickly create a prototype from their visual assets and test it with real or potential users. The practice of constant validation of design helps the team to develop better products for their users. Rapid prototyping is beneficial when the team wants to validate new features. Instead of guessing whether or not users will like the new feature, designers can create a prototype and invite users to try it.
As IDEO founder David Kelley famously said, "fail faster to succeed sooner." The earlier the team identifies the usability issues, the less expensive it will be to fix the issues. Rapid prototyping makes it easy to validate design during the early phases of product design.
The rapid prototyping technique motivates designers to create prototypes using existing design assets. As a result, a rapid prototype can be created on a relatively small budget.
Prototypes are interactive models, and when you show prototypes to stakeholders, you increase your chances of receiving more detailed feedback.
Apart from that, rapid prototyping changes the perception of design for product creators. A team that practices rapid prototyping sees a design not as a collection of static pages or screens but as an interactive experience. This perception impacts many design decisions the product team will make and help the team create user-centered products.
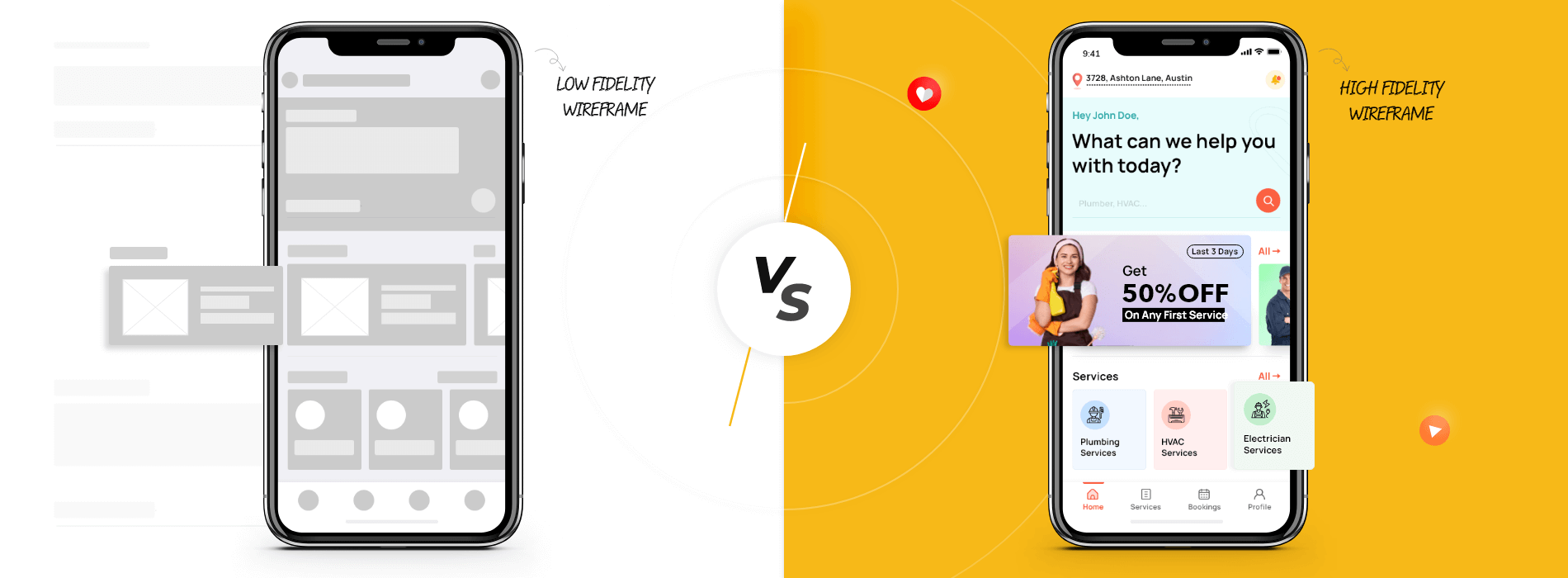
High-fidelity prototype of a mobile app. Image by Codiant.
Rapid prototyping is an iterative process that has three stages:
During this stage, the team defines what they want to include in a prototype. Every prototype should be created for a specific reason. For example, a team might want to validate the checkout flow, and they will make a prototype with steps that users go through when they buy a product. There is a big difference between creating a prototype for the whole app and creating a prototype for a particular user flow. Having a clear goal will make prototyping more focused.
A team often invests time in user research before creating a prototype. They try to understand the problems that users face when interacting with a product and, based on this information, choose user flows they want to prototype. For example, the team can focus on a particular edge case in the checkout flow, such as when a user chooses to use a specific payment method.
Experienced designers never rely on assumptions when they build a product; they always validate their hypotheses. The only way to understand whether a design works for users is to test a design with people who represent your target audience. Before the team validates the design, they define specific metrics to help the team understand how their design performs. For example, when it comes to checkout flow, the metrics can be time on task (how much time it takes for test participants to complete the operation) and error rate (number of errors that test participants face along the way).
At this stage, the team will analyze the testing results and identify areas where they need to introduce changes. For example, when the team sees that test participants make many mistakes when providing billing information, it will clearly indicate that this screen will require redesign. Once the team introduces all the necessary changes, they will build a new version of a prototype and conduct testing once again. The team will iterate until they achieve good results.
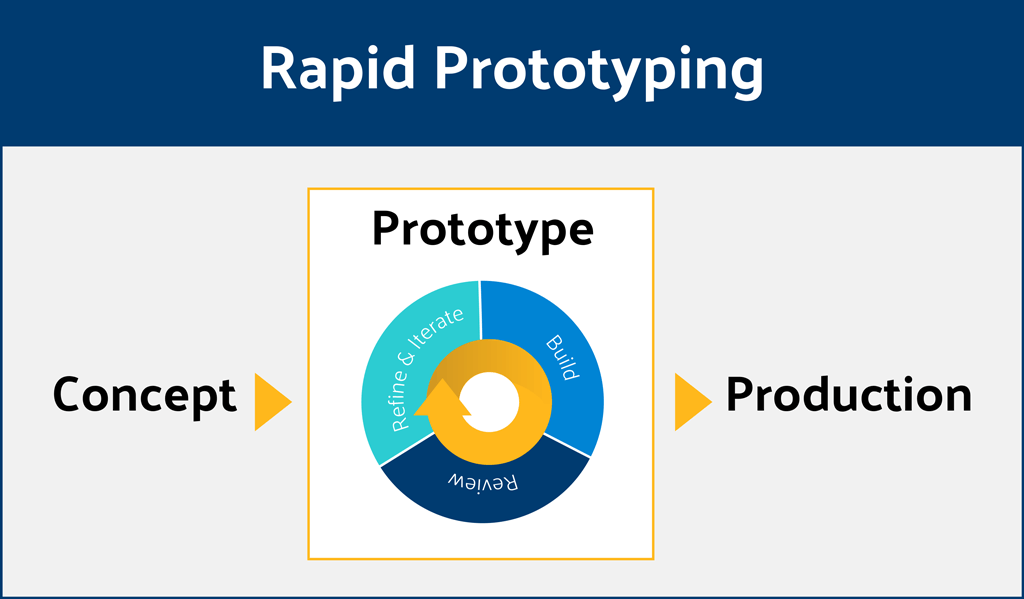
Before the team starts to build a prototype, it's vital to define the scope of prototyping and the level of fidelity a prototype should have. The scope of prototyping should be relevant to the goal you want to achieve. The fidelity of your prototype should match the fidelity of your thinking. For example, suppose you're in the early stages of product design. In that case, there is no need to create high-fidelity pixel-perfect prototypes because you will likely need to introduce many design changes along the way.
After you define the scope and fidelity, it's time to create an actual prototype. When it comes to rapid prototyping, you must strive to reuse as many artifacts as possible. Remember that each new extra element you need to design will increase the time required to build a prototype. Your goal is to create a prototype as fast as possible. Another thing to remember is that most of the time, it's not required to build a polished prototype. If you have time, it's always better to invest it in writing an actual copy for the screens rather than pushing pixels to achieve the pixel-perfect design.
Last but not least, always try to use digital tools when creating a prototype. Digital prototyping will make prototypes more reusable. Bringing a paper prototype to the meeting to receive feedback can be tedious; it's much easier to share a link to your prototype and receive the feedback in real-time.
After reading the previous sections, you might wonder, "But what is the difference between regular and rapid prototyping?" Regular and rapid prototyping have a lot of similarities, but they also have one key difference—the difference is the time required to go through the build-test-learn iteration. Rapid prototyping aims to reduce the time needed to complete the iteration. Instead of doing it for days, the team wants to achieve the same results in hours.
When the team practices rapid prototyping, they establish a strategy that allows them to iterate fast. The team prioritizes efforts (each prototype is created to achieve a specific goal) and cuts costs (the team tries to reuse as many assets as possible because creating new assets takes time). When the team masters rapid prototyping, it will have a significant advantage over other teams. The faster the team learns and introduces required chances, the quicker they can reach a state where they can release a decent product on the market.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is a process that relies on rapid iteration to get to a product that will provide the maximum value to the user. The faster the team can iterate the design, the more competitive it becomes in the market. Most of the time, the goal of rapid prototyping is not to showcase a pixel-perfect design but rather to validate hypotheses fast.